Client Vs Server Side Rendering React JS
Client Side Rendering
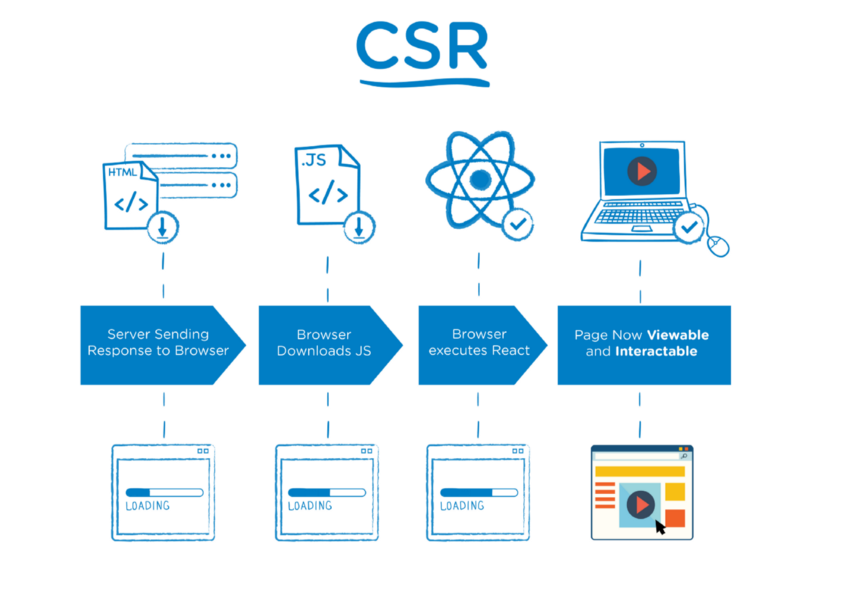
When we talk about client-side rendering,it’s about rendering content in the browser using JavaScript.
So instead of getting all the content from the HTML document itself, a simple HTML document with a JavaScript file in initial loading itself is received, which renders the rest of the site using the browser.
With client-side rendering, the initial page load is naturally a bit slow. However, after that, every subsequent page load is very fast. In this approach, communication with server happens only for getting the run-time data. Moreover, there is no need to reload the entire UI after every call to the server. The client-side framework manages to update UI with changed data by re-rendering only that particular DOM element.
Server Side Rendering
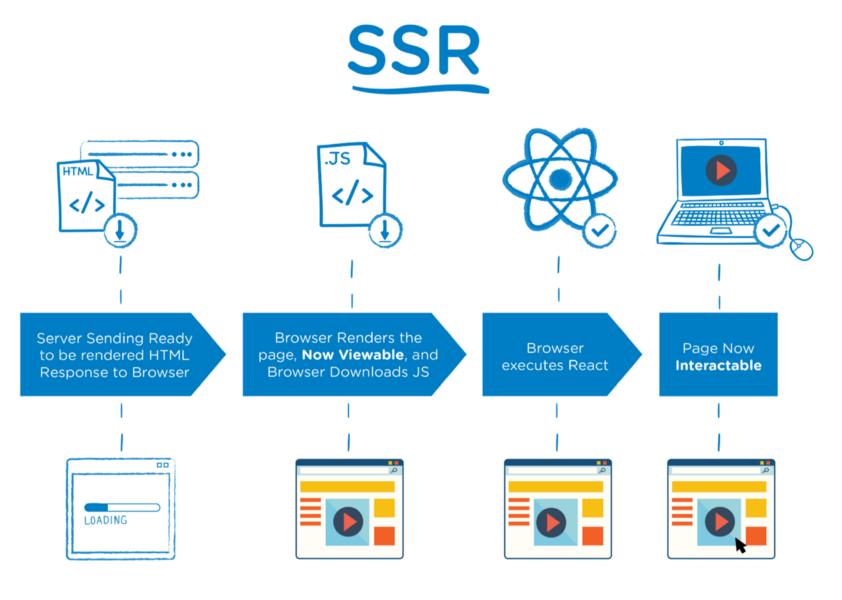
In server-side rendering when a user makes a request to a webpage, the server prepares an HTML page by fetching user-specific data and sends it to the user’s machine over the internet. Webpages are generated on your server for every request. This entire process of fetching data from the database, creating an HTML page and serve it to user is known as SSR.
Static Site Generation
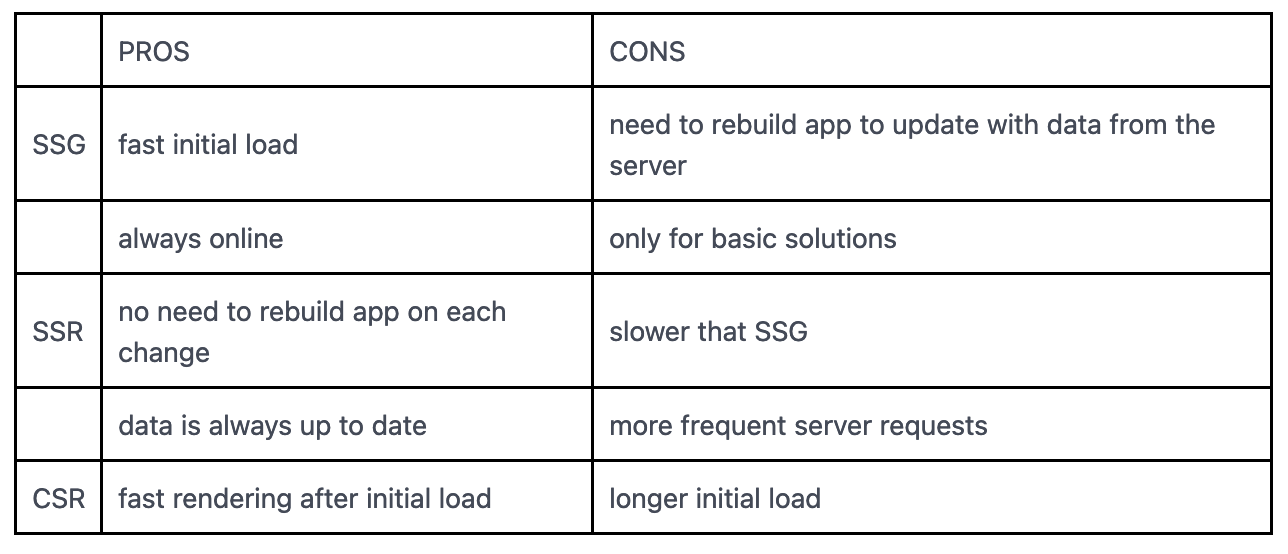
At build time, your app will fetch all the data required and compile it down to static webpages. After a production build is created, every request is going to reuse that statically generated HTML file. This provides the best performance and can easily be cached on a CDN.
Problems with React.js
React uses Client Side Rendering. With React, nothing gets displayed until all of your JavaScript loads. Your HTML is nearly empty and React injects your content in your HTML with JavaScript. This leads multiple problems:-
When the browser is loading the JavaScript, the screen is blank because
<div id="root"></div>does not show anything. Depending on the size of your JavaScript bundle, this could lead to your visitors staring at a white screen for a couple of seconds.Most SEO crawlers do not have JavaScript enabled. DuckDuckGo, Google, Bing and any other search engine would not actually know what is on your website since it requires JavaScript to display the content. You will not be ranked at all on Search Engines.
Methods for Prerendering using Next.js
Next.js offers (Server Side Rendering)SSR and (Static Site Generation)SSG using getStaticProps and getServerSideProps.
getStaticProps
getStaticProps is a server-side function that will only be called at build time. The build will then use the response from getStaticProps to generate a static webpage.
Since stale data is a problem with static generated pages, there is an option you can set to revalidate your static page and rebuild it if data changes. revalidate: 60 will check your data every 60 seconds and rebuild the page if needed.
Example Use:
// This function gets called at build time on server-side.
export async function getStaticProps() {
const res = await fetch('https://.../data');
const data = await res.json();
// By returning { props: data }, the Dashboard component
// will receive `data` as a prop at build time
return {
props: {
data
},
// Check if data changes every 60 seconds.
// Rebuild page if different
revalidate: 60
};
}
// data will be populated at build time by getStaticProps()
export default function Dashboard({ data }) {
return <div>{data}</div>;
}
getServerSideProps
getServerSideProps is similar to getStaticProps but is called every time the page loads instead of at build time. This ensures that all of your initial data is up to date on every load.
Since this is called on every load, you do not need to revalidate like getStaticProps. This also leads to a slower load time since you are no longer serving a static file, but have to rebuild on every load.
Example Use:
// This function gets called at build time on server-side.
export async function getServerSideProps() {
const res = await fetch('https://.../data');
const data = await res.json();
// By returning { props: data }, the Dashboard component
// will receive `data` as a prop at build time
return {
props: {
data
}
};
}
// data will be populated at build time by getServerSideProps()
export default function Dashboard({ data }) {
return <div>{data}</div>;
}
Benefits of using Next.js
Search engines can crawl the site for better SEO.
The initial page load is faster.
References:
Thanks for reading!!!
Abdul Wasea
Author